AppService to AzureSql using Managed Identity
I am guessing most of you, like me, have traditionally spun up an Azure Sql database, enabled Sql Authentication, stuffed that username and password into a connection string either in in Azure KeyVault or the appsettings.config/web.config.
I also assume if you have gotten to this post, you are either looking to change that approach on your own, have been told by your “security team” to do better or maybe some of both.
A lot of what I am going to detail below is lifted from here but with a UI and some screenshots to help.
To preface some of what I will show here, the example project is using the following:
dotnet 5EFCoreWindows App ServiceAzure Sql Serverless
I won’t be going into detail on how to setup EFCore using SqlServer as there are plenty of other examples, but I do want to focus on how to get your App Service talking to your Azure Sql Database using a managed identity.
Azure Sql Authentication Method
If you are just creating your Azure Sql Server now, make sure you select Use Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) authentication:
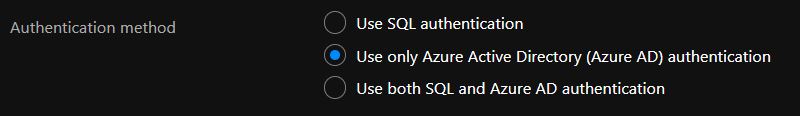
If you already have an Azure Sql Server and Database, go to your server and click on Settings -> Azure Active Directory:
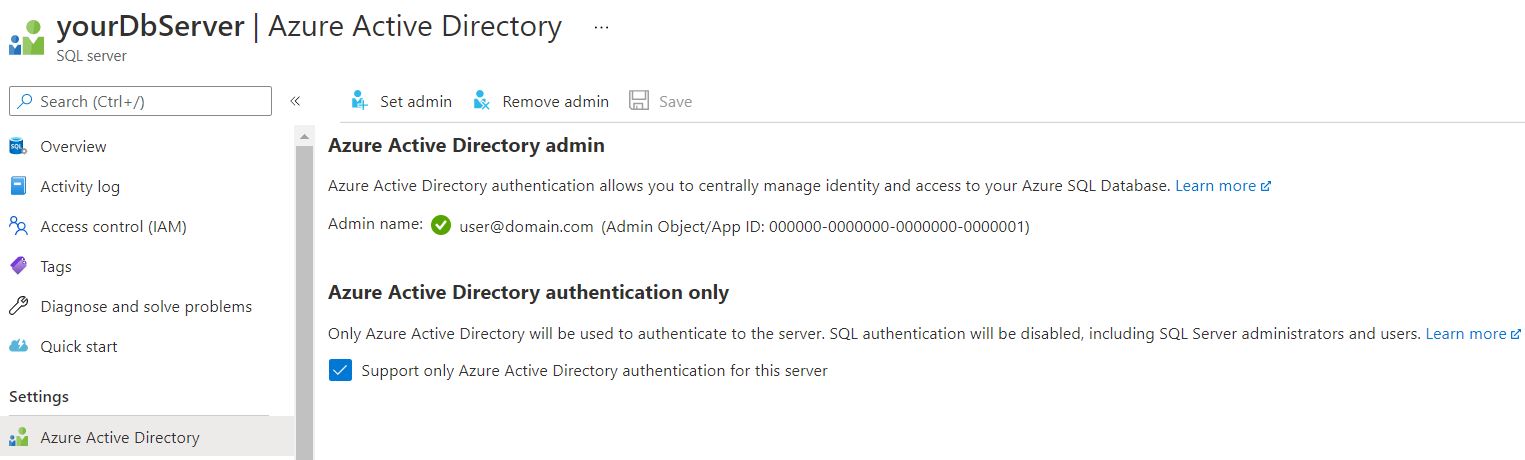
By selecting this option (for either) you are effectively disabling the Sql Authentication for the server. You will also have to assign an AD Admin for the server, make sure to assign an admin account you have access to as you will need it shortly…
Enabling Managed Identity
This should be pretty straightforward, go to your App Service, find Settings -> Identity and click Status -> On:
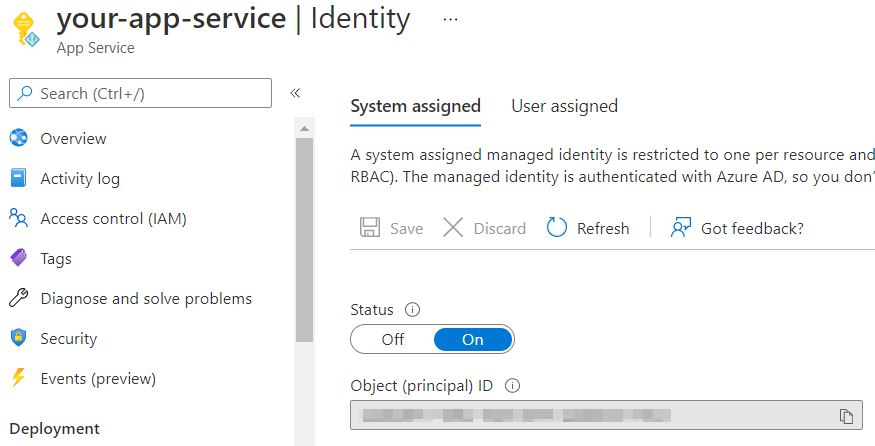
Your app service now has a proper identity.
Creating the Contained User
For this next step, you will need to make sure you have the server Firewall opened up enough for you to access the database and run some Sql, but you might as well grant access for the Azure Services too:
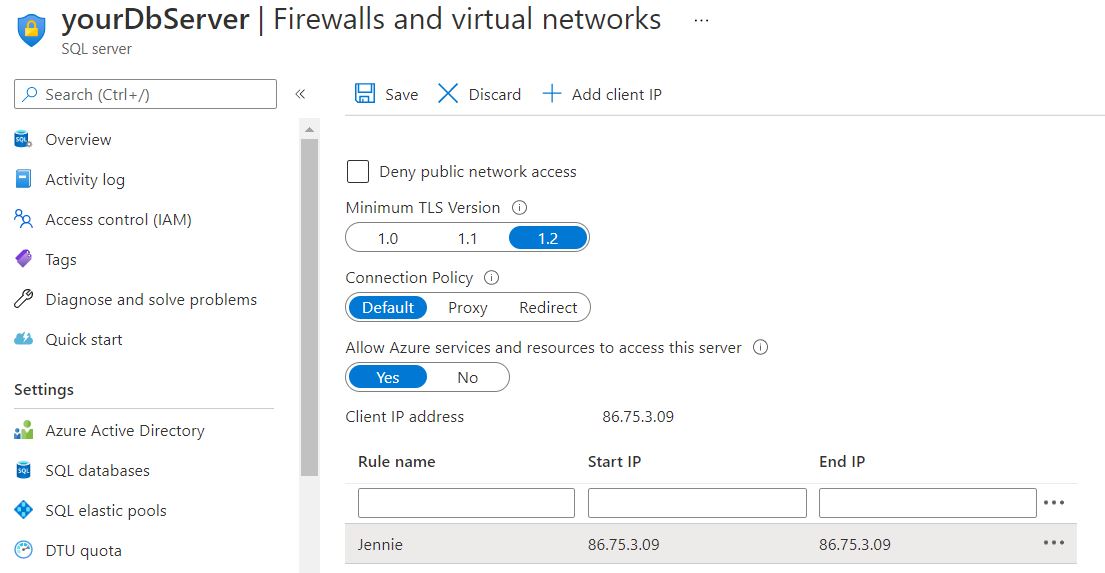
Now that you have line of sight to the server, open the database and you can either open up the Query Editor:
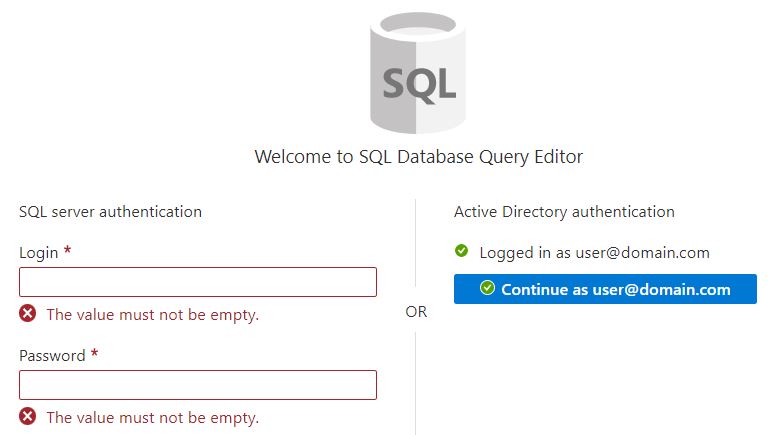
Or if you rather Sql Server Management Studio:
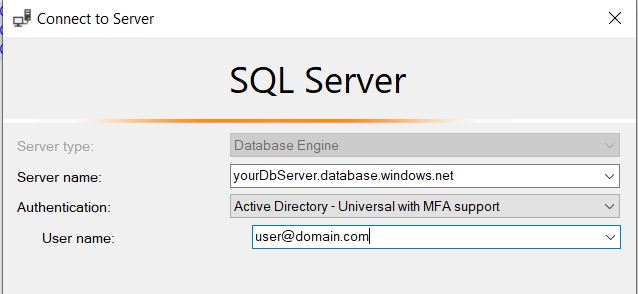
Regardless, you need to execute the following Sql:
-- WITH OBJECT_ID only needed if you have names not unique between app services and app registrations.
CREATE USER [your-app-service] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER WITH OBJECT_ID = 'a290ccc0-6142-4ff6-9620-7ea2393e6ed2';
ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD MEMBER [your-app-service];
ALTER ROLE db_datawriter ADD MEMBER [your-app-service];
ALTER ROLE db_ddladmin ADD MEMBER [your-app-service];
Where your-app-service is the actual name of your App Service in Azure (please make sure this is unique, both within App Services but also within Active Directory -> App Registrations).
You will get an error upon creation if it can not find the actual resource by name, so you won’t have to worry about botching it up yet… Also make sure to use applicable roles for your App Service.
Alright so we have Active Directory Authentication enabled for the Sql Server, a Managed Identity for our App Service, an actual user in the database for that Identity with roles, we have the database server Firewall accepting traffic from Azure resources, all we need now is a proper connection string:
ConnectionString
Server=tcp:yourDbServer.database.windows.net;Authentication=Active Directory Default; Database=YourDatabase;
And realistically, at this point, you should be done!
Additional note, I ran into some odd errors about authentication is 'unknown_type' specifically for the ConnectionString. It had seemed to be an issue with the Microsoft.Data.SqlClient that is included in the EFCore SqlServer package.
Simply by adding the Microsoft.Data.SqlClient package to the solution/project, to its latest version resolved this error. You may or may need to follow suit.
Happy Breaking.